Trove is Database as a Service for OpenStack. It’s designed to run entirely on OpenStack, with the goal of allowing users to quickly and easily utilize the features of a relational or non-relational database without the burden of handling complex administrative tasks. Cloud users and database administrators can provision and manage multiple database instances as needed. Initially, the service will focus on providing resource isolation at high performance while automating complex administrative tasks including deployment, configuration, patching, backups, restores, and monitoring.
Scope
- Setup Networking for Trove
- Deploy Trove Service
- Create Trove mgmt network
- Upload DB (mysql) Image.
- Create datastor and version
- Create database instance
- Test & Validation
- Database operations
Notes: I’m running kolla-ansible (2023.1). Adjust some configuration according your deployment tools.
Setup network for Trove
Trove has a very strange requirement where Trove talks to the instances via RabbitMQ using a common set of commands, which are translated into database server specific commands by the Trove guest-agent running on the instance. This is the biggest security concern because some Trove instance run on public IP and there is a possibility of privilege escalation to gain access to RabbitMQ. Here I am not going into that security discussion to architure. May be in next blog I will try to re-architecture to address security concern.
I have created dedicated VLAN for DBaaS for trove mgmt network. Trove DB instance (trove-guest-agent) will use this VLAN to talk to rabbitMQ. I’ll configure DBaaS VLAN and assign IP address to only openstack controller nodes. Following is my netplan configuration to get some idea.
output omitted...
# VxLAN for 10G Bond
bond10.11:
id: 11
link: bond10
dhcp4: false
dhcp6: false
mtu: 9000
addresses: [ 172.16.8.14/22 ]
# LBaaS (Octivia)
bond10.12:
id: 12
link: bond10
dhcp4: false
dhcp6: false
mtu: 1500
addresses: [ 172.17.8.14/22 ]
# DBaaS (Trove)
bond10.15:
id: 15
link: bond10
dhcp4: false
dhcp6: false
mtu: 1500
addresses: [ 172.19.8.14/22 ]
I have openstack network api network running on different interface and trove-mgmt-net running on different network. (To fix routing for trove guest agent to talk to rabbitMQ I’ve used host routes in trove-mgmt-net. you will see example in configuration section.)
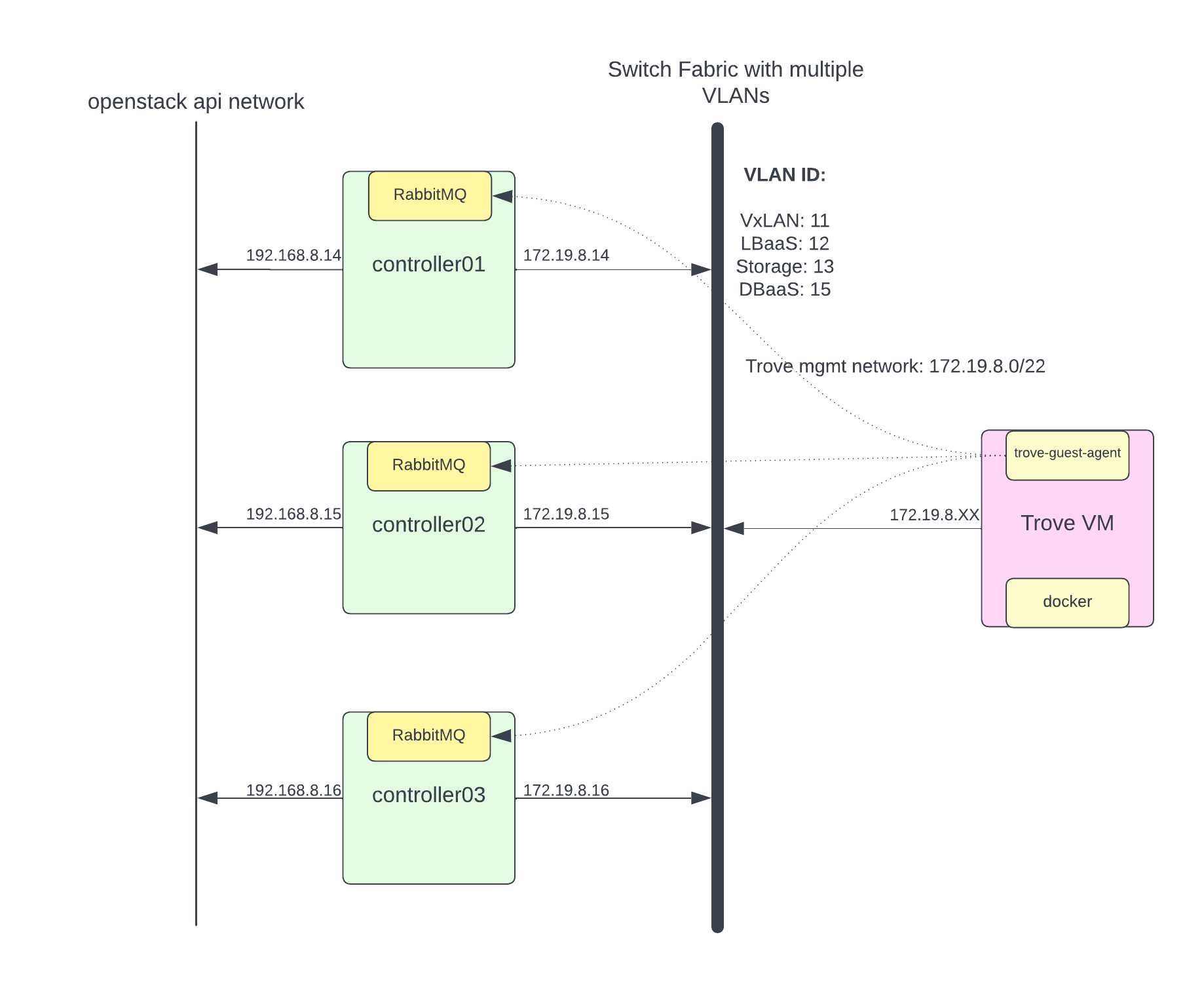
Deploy Trove Service
I am running kolla-ansible (2023.1 release). Possible this step is differ in your deployment environment.
In /etc/kolla/globals.yml
enable_trove: "yes"
Run kolla-ansible to deploy.
$ kolla-ansible -t multinode deploy -t trove,common,horizon
Configure Trove Service
NOTES : This patch https://review.opendev.org/c/openstack/kolla-ansible/+/863321/13still under pending review and because of that I have to create trove-mgmt-network and security group by hand.
Create trove mgmt network and subnet.
$ openstack network create --provider-physical-network physnet1 --provider-network-type vlan --provider-segment 15 trove-mgmt-net
$ openstack subnet create --subnet-range 172.19.8.0/22 --allocation-pool start=172.19.8.50,end=172.19.8.254 --network trove-mgmt-net trove-mgmt-subnet
NOTE: I have added host specific route in trove-mgmt-subnet because based on my network topology, because my openstack api network running on different network interface on openstack controller nodes.
$ openstack subnet show trove-mgmt-subnet
+----------------------+------------------------------------------------------+
| Field | Value |
+----------------------+------------------------------------------------------+
| allocation_pools | 172.19.8.50-172.19.8.254 |
| cidr | 172.19.8.0/22 |
| created_at | 2024-01-25T03:11:04Z |
| description | |
| dns_nameservers | |
| dns_publish_fixed_ip | None |
| enable_dhcp | True |
| gateway_ip | None |
| host_routes | destination='192.168.8.14/32', gateway='172.19.8.14' |
| | destination='192.168.8.15/32', gateway='172.19.8.15' |
| | destination='192.168.8.16/32', gateway='172.19.8.16' |
output omitted...
Create security group trove-sec-grp and allow ICMP and SSH ports and create ssh-key pair to access trove instance during troubleshooting. (You are going to create security-group and key inside trove service project. I mostly do this from Horizon GUI because its much easier).
Next configure trove to use trove network/security-group & key. Create followig file in kolla to push out changes.
/etc/kolla/config/trove.conf
[DEFAULT]
management_networks = ee2a2a81-178c-4d79-867b-8baf53ec236d
nova_keypair = trove-ssh-key
management_security_groups = 451e4b4a-58b4-4e9f-84a8-5bdb21e34cd5
/etc/kolla/config/trove-guestagent.conf
[DEFAULT]
transport_url = rabbit://openstack:<RABBITMQ_PASSWORD>@192.168.8.14:5672,openstack:<RABBITMQ_PASSWORD>@192.168.8.15:5672,openstack:<RABBITMQ_PASSWORD>@192.168.8.16:5672//
control_exchange = trove
root_grant = ALL
root_grant_option = True
debug = False
[oslo_messaging_rabbit]
heartbeat_in_pthread = false
amqp_durable_queues = true
rabbit_quorum_queue = true
NOTES: I have created trove-guestagent.conf file to override my changes like RabbitMQ IP. 192.168.8.X is my openstack API network where rabbitMQ running.
Deploy changes.
$ kolla-ansible -i multinode reconfigure -t trove
Deploy Trove Image & Datastore version
Download trove image for testing. (For production you should build your own image)
$ wget https://tarballs.opendev.org/openstack/trove/images/trove-master-guest-ubuntu-jammy.qcow2
Upload image in glance, the image is assigned tags that will be used when creating datastore version.
$ openstack image create Trove-Ubuntu --disk-format qcow2 --container-format bare --public --tag trove --file trove-master-guest-ubuntu-jammy.qcow2
Create database version. You need to create at least one datastore version for each type of database supported. This example creates a datastore version for MySQL 5.7.29:
$ openstack datastore version create 5.7.29 mysql mysql "" --image-tags trove,mysql --active --default --version-number 5.7.29
Verify datastore version.
$ openstack datastore version list mysql
+--------------------------------------+--------+---------+
| ID | Name | Version |
+--------------------------------------+--------+---------+
| 0b218550-a28c-4cb7-b907-ecac89a27b5f | 5.7.29 | 5.7.29 |
+--------------------------------------+--------+---------+
Validation and Testing
Create mysql database instance. (–is-public will assign public network for outside world access)
$ openstack database instance create my_db \
--flavor m1.medium \
--size 10 \
--nic net-id=81ce26ec-1151-4960-b3ca-bf529e6296b2 \
--database testdb \
--users spatel:mypassword \
--datastore mysql \
--datastore-version 5.7.29 \
--is-public \
--allowed-cidr 0.0.0.0/0
Check status of database instance. Voila!!
$ openstack database instance list
+--------------------------------------+-------+-----------+-------------------+--------+------------------+--------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------+-----------+------+------+
| ID | Name | Datastore | Datastore Version | Status | Operating Status | Public | Addresses | Flavor ID | Size | Role |
+--------------------------------------+-------+-----------+-------------------+--------+------------------+--------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------+-----------+------+------+
| 95949d3e-2478-435f-b178-b5224854434d | my_db | mysql | 5.7.29 | ACTIVE | HEALTHY | True | [{'address': '10.0.0.205', 'type': 'private', 'network': | 3 | 10 | |
| | | | | | | | '81ce26ec-1151-4960-b3ca-bf529e6296b2'}, {'address': '202.202.202.202', 'type': | | | |
| | | | | | | | 'public'}] | | | |
+--------------------------------------+-------+-----------+-------------------+--------+------------------+--------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------+-----------+------+------+
Let’s access it from public network and verify database.
$ mysql -h 202.202.202.202 -u spatel -p
Enter password:
Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 20
Server version: 5.7.29 MySQL Community Server (GPL)
Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
MySQL [(none)]> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| testdb |
+--------------------+
2 rows in set (0.14 sec)
MySQL [(none)]>
Database operations & User management using Trove API
You can list database users.
$ openstack database user list my_db
+--------+------+-----------+
| Name | Host | Databases |
+--------+------+-----------+
| spatel | % | testdb |
+--------+------+-----------+
Create new user for testdb.
$ openstack database user create my_db newuser userpass --databases testdb
$ openstack database user list my_db
+---------+------+-----------+
| Name | Host | Databases |
+---------+------+-----------+
| newuser | % | testdb |
| spatel | % | testdb |
+---------+------+-----------+
Create new database.
$ openstack database db create my_db newdb
$ openstack database db list my_db
+--------+
| Name |
+--------+
| newdb |
| testdb |
+--------+
Manage access to databases using trove api.
$ openstack database user grant access my_db newuser newdb
$ openstack database user show access my_db newuser
+--------+
| Name |
+--------+
| newdb |
| testdb |
+--------+
Troubleshooting
Sometime you would like to get on vm instance to check logs of trove-guest-agent or docker container etc.
First find out VM instance IP address of trove-mgmt-network where your DB running.
$ openstack server list --project service --name my_db
+--------------------------------------+-------+--------+-------------------------------------------------------------------+--------------+-----------+
| ID | Name | Status | Networks | Image | Flavor |
+--------------------------------------+-------+--------+-------------------------------------------------------------------+--------------+-----------+
| 5e60e685-14a9-4e23-9aaa-7dd5aa82cfd9 | my_db | ACTIVE | demo-net=10.0.0.205, 202.202.202.202; trove-mgmt-net=172.19.8.172 | Trove-Ubuntu | m1.medium |
+--------------------------------------+-------+--------+-------------------------------------------------------------------+--------------+-----------+
SSH to 172.19.8.172 from controller node because it has IP address of that subnet. (make sure you are using right ssh-key for instance)
$ ssh 172.19.8.172 -l ubuntu
ubuntu@my-db:~$ sudo su -
root@my-db:~#
Check logs of trove agent.
$ journalctl -u guest-agent.service -f
Check docker and logs because mysql database running inside docker container.
$ docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
3a98e2a23396 mysql:5.7.29 "docker-entrypoint.s…" 36 minutes ago Up 36 minutes 0.0.0.0:3306->3306/tcp, :::3306->3306/tcp, 33060/tcp database
Check docker logs of database container.
$ docker logs database
Enjoy!!!
Brak komentarzy:
Prześlij komentarz